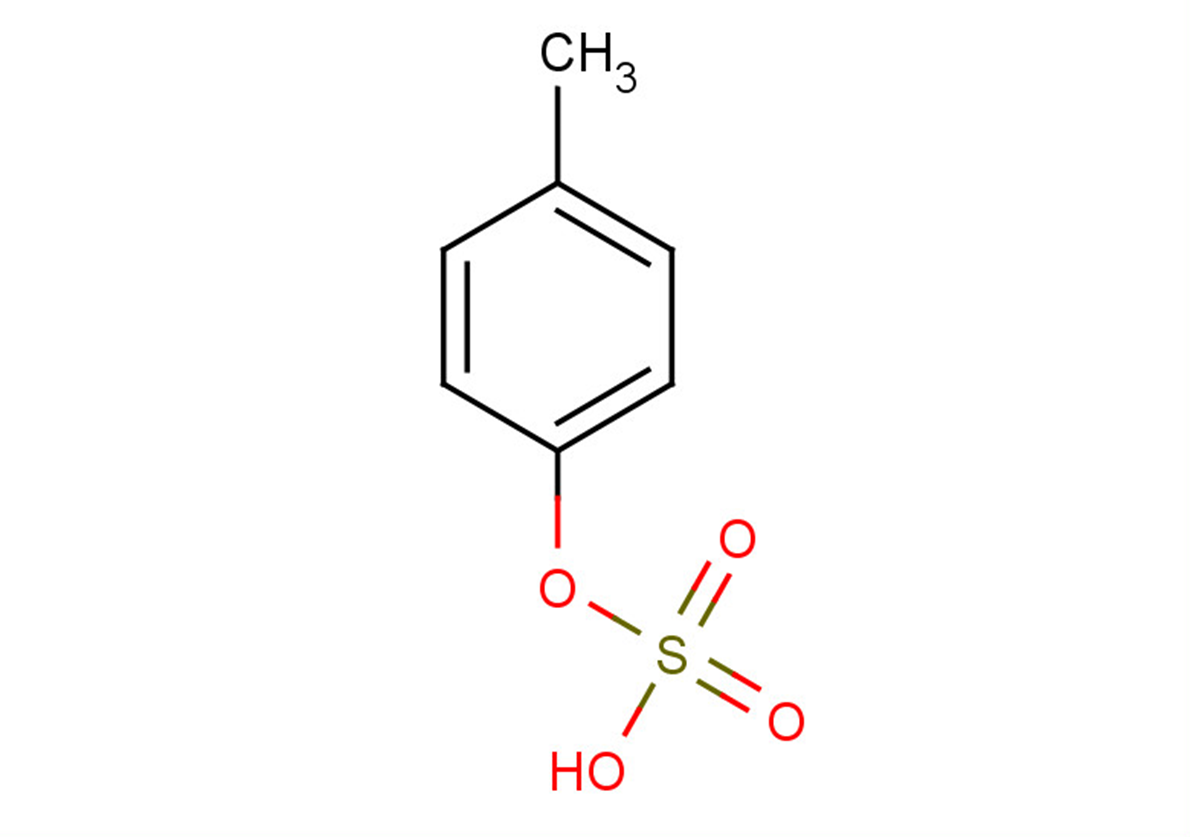
p-Cresyl sulfate
CAS No. 3233-58-7
p-Cresyl sulfate( —— )
Catalog No. M24256 CAS No. 3233-58-7
The p-Cresol is a protein-bound uremic retention solute. Free p-Cresol was found to be a cardiovascular risk factor in non-diabetic hemodialysis patients.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 110 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 177 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 312 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 464 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 662 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 1332 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Namep-Cresyl sulfate
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionThe p-Cresol is a protein-bound uremic retention solute. Free p-Cresol was found to be a cardiovascular risk factor in non-diabetic hemodialysis patients.
-
DescriptionThe p-Cresol is a protein-bound uremic retention solute. Free p-Cresol was found to be a cardiovascular risk factor in non-diabetic hemodialysis patients.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number3233-58-7
-
Formula Weight188.2
-
Molecular FormulaC7H8O4S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 250 mg/mL (1328.37 mM)
-
SMILESCC1=CC=C(OS(=O)(O)=O)C=C1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Meijers B K I, Bammens B, De Moor B, et al. Free p-cresol is associated with cardiovascular disease in hemodialysis patients. Kidney international, 2008, 73(10): 1174-1180.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Buparvaquone
Buparvaquone is a hydroxynaphthoquinone antiprotozoal drug related to parvaquone and atovaquone.
-
4-Biphenylcarboxylic...
4-Biphenylcarboxylic acid is a useful organic compound for research related to life sciences.
-
(R)-3-Hydroxybutanoi...
3-hydroxybutyric acid is involved in the synthesis and degradation of ketone bodies. Like the other ketone bodies (acetoacetate and acetone) levels of beta-hydroxybutyrate are raised in the blood and urine in ketosis. Beta-hydroxybutyrate is a typical partial-degradation product of branched-chain amino acids (primarily valine) released from muscle for hepatic and renal gluconeogenesis.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


